您现在的位置是:网站首页> 编程资料编程资料
解析spark源码yarn-cluster模式任务提交_linux shell_
![]() 2023-05-26
547人已围观
2023-05-26
547人已围观
简介 解析spark源码yarn-cluster模式任务提交_linux shell_
一,运行命令
bin/spark-submit \ --master yarn \ --deploy-mode cluster \ --class org.apache.spark.examples.SparkPi \ examples/jars/spark-examples_2.11-2.3.1.3.0.1.0-187.jar
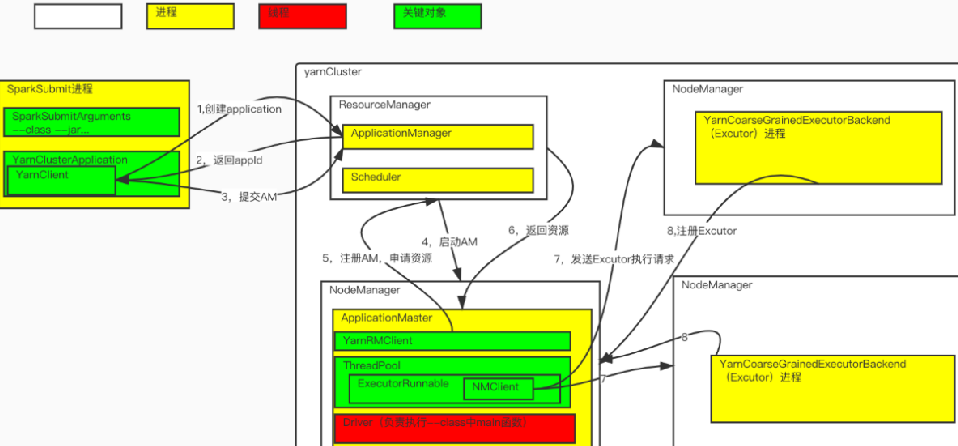
二,任务提交流程图
三,启动脚本
查看spark-submit 脚本文件,程序入口为
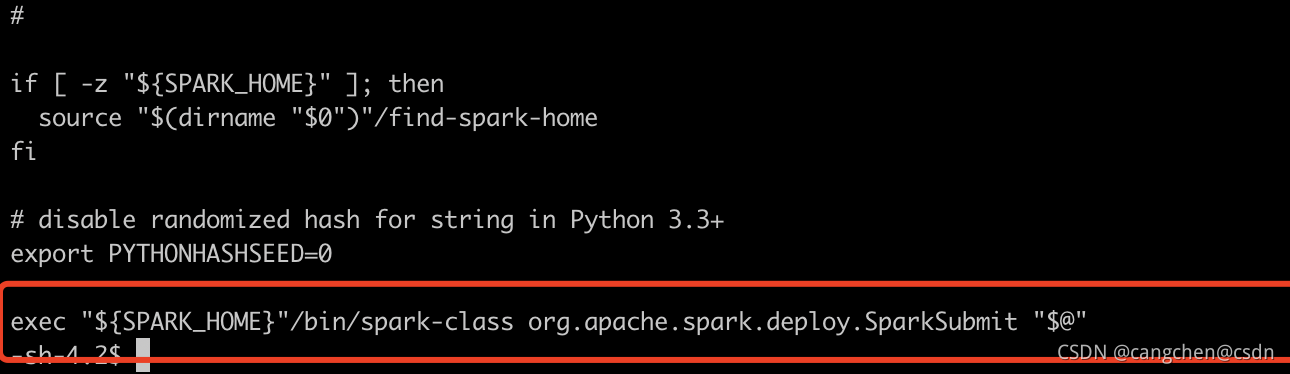
exec "${SPARK_HOME}"/bin/spark-class org.apache.spark.deploy.SparkSubmit "$@“ 查看${SPARK_HOME}"/bin/spark-class可知该脚本执行了java -cp main-class 命令启动了一个java进程,进程名为SparkSubmit,main函数在主类org.apache.spark.deploy.SparkSubmit中。
实际执行的具体命令为:
/etc/alternatives/jre/bin/java -Dhdp.version=3.0.1.0-187 -cp /usr/hdp/3.0.1.0-187/spark2/conf/:/usr/hdp/3.0.1.0-187/spark2/jars/*:/usr/hdp/3.0.1.0-187/hadoop/conf/ -Xmx1g org.apache.spark.deploy.SparkSubmit --master yarn --class org.apache.spark.examples.SparkPi examples/jars/spark-examples_2.11-2.3.1.3.0.1.0-187.jar
四,程序入口类org.apache.spark.deploy.SparkSubmit
该类有个伴生对象,其中有main函数,创建了SparkSubmit对象并执行doSubmit();
override def main(args: Array[String]): Unit = { val submit = new SparkSubmit() {...} submit.doSubmit(args) } doSubmit 解析args参数,封装到appArgs:SparkSubmitArguments对象中,然后执行submit(appArgs, uninitLog)。
def doSubmit(args: Array[String]): Unit = { // Initialize logging if it hasn't been done yet. Keep track of whether logging needs to // be reset before the application starts. val uninitLog = initializeLogIfNecessary(true, silent = true) val appArgs = parseArguments(args) if (appArgs.verbose) { logInfo(appArgs.toString) } appArgs.action match { case SparkSubmitAction.SUBMIT => submit(appArgs, uninitLog) case SparkSubmitAction.KILL => kill(appArgs) case SparkSubmitAction.REQUEST_STATUS => requestStatus(appArgs) case SparkSubmitAction.PRINT_VERSION => printVersion() } } submit(appArgs, uninitLog) 调用 runMain(args: SparkSubmitArguments, uninitLog: Boolean)
private def runMain(args: SparkSubmitArguments, uninitLog: Boolean): Unit = { val (childArgs, childClasspath, sparkConf, childMainClass) = prepareSubmitEnvironment(args) . . . try { mainClass = Utils.classForName(childMainClass) } catch {...} val app: SparkApplication = if (classOf[SparkApplication].isAssignableFrom(mainClass)) { mainClass.getConstructor().newInstance().asInstanceOf[SparkApplication] } else { new JavaMainApplication(mainClass) } . . . try { app.start(childArgs.toArray, sparkConf) } catch { case t: Throwable => throw findCause(t) } } 这里mainClass十分重要,先判读mainClass是否是SparkApplication的子类,如果是则通过反射调用其构造器创建对象;
如果不是则创建一个JavaMainApplication(是SparkApplication的子类)对象并在其override def start(args: Array[String], conf: SparkConf)函数中利用反射执行mainClass中main函数。
SparkApplication创建完毕后执行其start(childArgs.toArray, sparkConf) 方法。
/** * Entry point for a Spark application. Implementations must provide a no-argument constructor. */ private[spark] trait SparkApplication { def start(args: Array[String], conf: SparkConf): Unit } /** * Implementation of SparkApplication that wraps a standard Java class with a "main" method. * * Configuration is propagated to the application via system properties, so running multiple * of these in the same JVM may lead to undefined behavior due to configuration leaks. */ private[deploy] class JavaMainApplication(klass: Class[_]) extends SparkApplication { override def start(args: Array[String], conf: SparkConf): Unit = { val mainMethod = klass.getMethod("main", new Array[String](0).getClass) if (!Modifier.isStatic(mainMethod.getModifiers)) { throw new IllegalStateException("The main method in the given main class must be static") } val sysProps = conf.getAll.toMap sysProps.foreach { case (k, v) => sys.props(k) = v } mainMethod.invoke(null, args) } } 如果**–deploy-mode** 是client mainClass的值由命令行参数 –class 决定,也就是org.apache.spark.examples.SparkPi。
这种情况下会在当前虚拟机中执行客户端代码,如果是其它条件情况会比较复杂。
以上文指定的运行命令为例,这里mainClass是org.apache.spark.deploy.yarn.YarnClusterApplication类class对象。
private[deploy] val YARN_CLUSTER_SUBMIT_CLASS = "org.apache.spark.deploy.yarn.YarnClusterApplication" ... if (isYarnCluster) { childMainClass = YARN_CLUSTER_SUBMIT_CLASS if (args.isPython) { childArgs += ("--primary-py-file", args.primaryResource) childArgs += ("--class", "org.apache.spark.deploy.PythonRunner") } else if (args.isR) { val mainFile = new Path(args.primaryResource).getName childArgs += ("--primary-r-file", mainFile) childArgs += ("--class", "org.apache.spark.deploy.RRunner") } else { if (args.primaryResource != SparkLauncher.NO_RESOURCE) { childArgs += ("--jar", args.primaryResource) } childArgs += ("--class", args.mainClass) } if (args.childArgs != null) { args.childArgs.foreach { arg => childArgs += ("--arg", arg) } } } 五,org.apache.spark.deploy.yarn.YarnClusterApplication类
该类在spark-yarn包中。
org.apache.spark spark-yarn_${scala.version} ${spark.version}
开始执行其override def start(args: Array[String], conf: SparkConf) 方法。
private[spark] class YarnClusterApplication extends SparkApplication { override def start(args: Array[String], conf: SparkConf): Unit = { // SparkSubmit would use yarn cache to distribute files & jars in yarn mode, // so remove them from sparkConf here for yarn mode. conf.remove(JARS) conf.remove(FILES) new Client(new ClientArguments(args), conf, null).run() } } SparkSubmi进程中创建一个客户端Client,该类是一个代理类其中包括YarnClient,执行run() 方法。
提交Application给yarn集群ResourceManager,提交成功后返回appid,
如果spark.submit.deployMode=cluster&&spark.yarn.submit.waitAppCompletion=true,
SparkSubmit进程会定期输出appId日志直到任务结束(monitorApplication(appId)),否则会输出一次日志然后退出。
def run(): Unit = { this.appId = submitApplication() if (!launcherBackend.isConnected() && fireAndForget) { val report = getApplicationReport(appId) val state = report.getYarnApplicationState logInfo(s"Application report for $appId (state: $state)") logInfo(formatReportDetails(report)) if (state == YarnApplicationState.FAILED || state == YarnApplicationState.KILLED) { throw new SparkException(s"Application $appId finished with status: $state") } } else { val YarnAppReport(appState, finalState, diags) = monitorApplication(appId) if (appState == YarnApplicationState.FAILED || finalState == FinalApplicationStatus.FAILED) { diags.foreach { err => logError(s"Application diagnostics message: $err") } throw new SparkException(s"Application $appId finished with failed status") } if (appState == YarnApplicationState.KILLED || finalState == FinalApplicationStatus.KILLED) { throw new SparkException(s"Application $appId is killed") } if (finalState == FinalApplicationStatus.UNDEFINED) { throw new SparkException(s"The final status of application $appId is undefined") } } } 继续跟踪submitApplication()
def submitApplication(): ApplicationId = { ResourceRequestHelper.validateResources(sparkConf) var appId: ApplicationId = null try { launcherBackend.connect() yarnClient.init(hadoopConf) yarnClient.start() logInfo("Requesting a new application from cluster with %d NodeManagers" .format(yarnClient.getYarnClusterMetrics.getNumNodeManagers)) // Get a new application from our RM val newApp = yarnClient.createApplication() val newAppResponse = newApp.getNewApplicationResponse() appId = newAppResponse.getApplicationId() // The app staging dir based on the STAGING_DIR configuration if configured // otherwise based on the users home directory. val appStagingBaseDir = sparkConf.get(STAGING_DIR) .map { new Path(_, UserGroupInformation.getCurrentUser.getShortUserName) } .getOrElse(FileSystem.get(hadoopConf).getHomeDirectory()) stagingDirPath = new Path(appStagingBaseDir, getAppStagingDir(appId)) new CallerContext("CLIENT", sparkConf.get(APP_CALLER_CONTEXT), Option(appId.toString)).setCurrentContext() // Verify whether the cluster has enough resources for our AM verifyClusterResources(newAppResponse) // Set up the appropriate contexts to launch our AM val containerContext = createContainerLaunchContext(newAppResponse) val appContext = createApplicationSubmissionContext(newApp, containerContext) // Finally, submit and monitor the application logInfo(s"Submitting application $appId to ResourceManager") yarnClient.submitApplication(appContext) launcherBackend.setAppId(appId.toString) reportLauncherState(SparkAppHandle.State.SUBMITTED) appId } catch { case e: Throwable => if (stagingDirPath != null) { cleanupStagingDir() } throw e } 该方法做了如下工作(对应于任务提交流程图中的1,2,3):
1,向ResourceManager发送请求创建A
相关内容
- ansible执行shell脚本的方法_linux shell_
- Shell获取当前正在执行脚本的绝对路径_linux shell_
- 入门shell脚本基础及原理_linux shell_
- Linux自定义防误删脚本的思路与测试_linux shell_
- 学习Linux网络编程基本函数_linux shell_
- Linux网络设置详情_linux shell_
- Shell脚本中$符号的几种用法小结_linux shell_
- 浅谈Shell脚本参数与交互及常见问题_linux shell_
- shell脚本读取命令行参数的实现_linux shell_
- 反弹shell的几种姿势小结_linux shell_





